Macronutrient Calculator & Micronutrient Calculator by Upfit
With the Nutrient Calculator from Upfit you can easily and quickly calculate your perfect macronutrient and micronutrient composition for weight loss, clean eating, muscle building, or definition. If you wish, you can also receive recipes for your personal calorie and nutritional needs via email.
100% free
Science-based
Incl. Calculation of Macro- & Micronutrients
This is how our Nutritional Calculator works
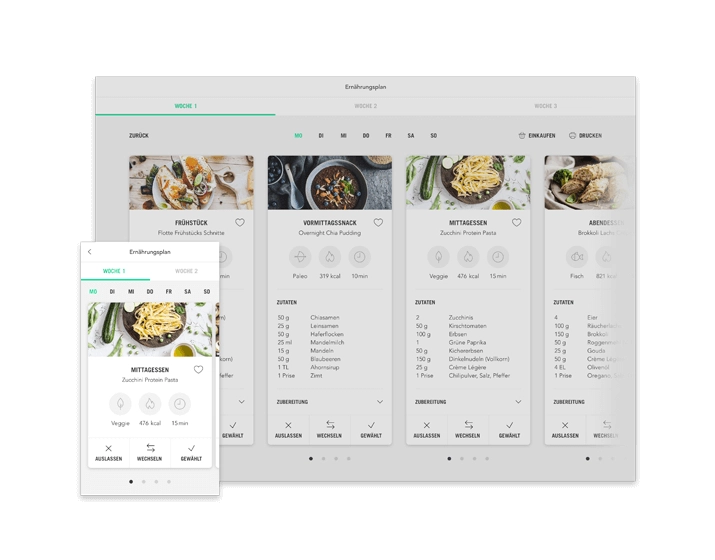
The free Nutrient Calculator from Upfit not only calculates your optimal nutrient requirement, but also many other details. It calculates your ideal nutrient distribution at the macro and micro level as well as the calories required for you and your personal goal. That makes it the best free nutrient calculator on the net. It also suggests suitable recipes for your personal calorie needs. For this, the calculator collects various pieces of key data, such as your weight, height, and physical activity level. Based on a scientifically sound basis, the ideal values are then calculated within a few seconds.
Macronutrients - Energy for The Body
Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are so-called “macros”, which supply our bodies with energy. In metabolic processes, the individual components of our food are broken down by enzymes. Every action of our body – be it breathing, running, or even our hearts beating – consumes energy. This energy comes from macronutrients. While energy is a term that comes from physics, in nutritional jargon this energy is more commonly called kilocalories (kcal). One kilocalorie is one unit of this energy. These calories are for the human body, what gasoline is for a sports car.
Are all macronutrients the same?
Each macronutrient provides different amounts of energy. One gram of carbohydrates or proteins provide about 4 kcal. On the other hand, one gram of fat provides you 9 kcal. For this reason, one speaks often of “fat reserves”. Fat is a very high-energy macronutrient. It is stored in order to be able to supply the body with energy under prolonged stress. Carbohydrates, on the other hand, are primarily consumed during intensive exercise. Read more about macronutrients and what they are good for in our Nutrient Section.
In short, the body needs macronutrients to provide energy for everyday life. Because every metabolism and every organism is different, everyone requires different macronutrients. Especially with different goals like losing weight or building muscle, the distribution of these macros is often crucial for success. Other influences include gender, body type, or weight. Therefore, it is important to adapt your diet to your personal needs.
Distribution of Macronutrients - It's all in the right mixture!
Especially because we have very different everyday requirements (low activity office jobs versus heavy weight training) we should adjust our macronutrients according to your personal lifestyles and goals. With the Macronutrient Calculator you can easily determine your personal need for carbohydrates, protein and fats.
To adjust your diet to be perfect for your body, you would have to read nutritional tables, weigh your food, and calculate your nutrients every day. This often takes a lot of time. The Upfit diet Plans do this for you. Every day you get recipes that are tailored to your needs. Whether you’re building muscle, losing weight, or just eating a healthy, clean diet.
If you like the Calculator, you can easily integrate it on your own webpage.
Micronutrients - Vitamins, Minerals & Co.
In times of low-carb or high-fat diets, micronutrients are often forgotten. That does not mean that they are not just as important! The micronutrients include primarily vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals.
Vitamins
Except for vitamin D, the body is unable to make vitamins on its own. This explains why a balanced diet is so important to our body. The right interaction of micros and macros is critical for your goals. For example, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 are responsible for the processing of proteins.
A healthy person can provide his body with all the vitamins through a balanced diet. Supplementation is usually not necessary in a healthy diet.
The following list describes which vitamins is found in which foods. However, the selected foods general contain many more health-promoting substances and are therefore suitable for a balanced diet.
- Vitamin A: carrots, cantaloupe melon, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, apricots, spinach, eggs
- Vitamin C: guava, citrus fruits and juices, papaya, kiwi, broccoli, strawberries, tomatoes, potatoes
- Vitamin D: salmon, tuna, sardines, mackerel, egg yolk, orange juice
- Vitamin E: nuts, seeds, spinach, kiwi, vegetable oils
- Vitamin K: spinach, cabbage, broccoli, chard
- Vitamin B1: sunflower seeds, pasta, meat, fish, beans, green peas, corn, soybeans
- Vitamin B2: eggs, lean meat, vegetables, nuts, dairy products, cereals
- Vitamin B3: Dairy products, poultry, fish, lean meat, nuts, eggs, bread, cereals
- Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid): mushrooms, sunflower seeds, calf’s liver, eggs, fish, dairy products, whole grain cereals, beans
- Biotin: eggs, fish, milk, dairy products, soy products, nuts, chard, cereals, beans
- Vitamin B6: beans, bananas, nuts, eggs, meat (poultry), potatoes
- Vitamin B12: meat, eggs, fish (trout and salmon), dairy products
- Folsäure: avocado, green peas, cereals, liver, green vegetables, certain types of bread
Minerals
Minerals are important especially for the metabolism. They regulate cell activity and are part of the enzymatic processes in the body. They are also important for the health of other body structures such as teeth and bones. A well-known example is the calcium in the milk, which for years was considered a guarantee for strong bones. Minerals also influence acid-base balance as well as the heart rhythm. You can find more about minerals in our Coach Articles.
Why are micronutrients so important to my diet?
Although micronutrients do not provide the body with energy, they are vital. Only when the body is sufficiently supplied with all nutrients, with it works truly effectively. Micronutrients not only help you to lose weight or build muscle, they also prevent illnesses and makes you feel better. The right combination of both types of nutrients you can imagine as follows: Your body is a vessel filled with water, the macronutrients in this example. A micronutrient deficiency is a hole in the bottom of this vessel. Only when both micro and macronutrients are available in sufficient quantities does your body work perfectly.
What is Upfit's Nutrient Calculator based on?
In order to find out how many calories you should eat and from which nutritional components, we rely on a strong scientific basis and specific empirical values. To calculate your energy needs, we use the best and most accurate formula – the so-called Harris-Benedict formula. First we determine your basal metabolic rate (1). Then we determine your physical activity level, known as the PAL factor), we then factor in your personal nutritional goal: either an energy surplus (muscle building), energy balance (maintaining weight) or an energy deficit (losing weight, definition). We divide the resulting amount of calories into the 3 macronutrient groups on according to the latest scientific findings (2, 3, 4) and based on the experience of expert practicing coaches and dietitians. The recommendations on micronutrient intake are based on the guidelines of the World Health Organization (5) and the German Nutrition Society (6). The body weight rating in relation to height is expressed in terms of the BMI value based on the research of Adolphe Quetelet and Ignaz Kaup (7). So we can guarantee a secure, working and efficient tool that optimally supports you on your way to realizing your dream body.
Sources
- Amirkalali, B. et al. (2008). Measuring or predicting resting energy expenditure. Indian Journal of Medical Science Vol. 62 No. 7. S. 283-290.
- Arciero, P. et al. (2016). Protein-Pacing Caloric-Restriction enhances body composition similarly in obese men and women during weight loss and sustains efficacy during long term weight maintenance. Nutrients. 2016 Aug 8 (8), S. 476 ff.
- Petersen, J. (2017). Attenuating the side effects of caloric restriction through exercise and increased protein intake. Nutrition & health sciences dissertations & theses (71). University of Nebraska – Lincoln.
- Helms, E. et al. (2014). A systematic review of dietary protein during caloric restriction in resistance trained lean athletes: a case for higher intakes. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism (24), S. 127-138.
- Weltgesundheitsorganisation (WHO). Link: http://www.euro.who.int/de/home
- Deutschen Gesellschaft für Ernährung (DGE). Link: https://www.dge.de/
- Quételet, A. (1871): L’anthropométrie ou le mesure des differentes facultés de l’homme. Bruxelles: Muquardt, C.